Configure Gitlab Service Discovery
Gitlab 에서 Consul 을 통한 Service Discovery 에 대한 설명 페이지
About Consul
- Consul 에서 제공하는 Service Discovery 기능은 크게 3가지가 있으며 이를 구분해 보면 아래와 같음
- Register Service
-
App 이 실행되는 위치에 Consul Client 를 설치하고 Service Definition 을 작성 후 Consul Client 를 실행시켜 Service 를 등록
# Consul Client $ sudo su $ cd /tmp $ sudo cat <<EOF > web.json { "service": { "name": "web", "port": 80 } } EOF # Register Service By Command $ consul services register web.json # Deregister Service By Command $ consul services deregister web.json # Register Service By API $ curl \ --request PUT \ --data @web.json https://<SERVER_IP>:8500/v1/agent/service/register # Deregister Service By API $ curl \ --request PUT \ --data @web.json https://<SERVER_IP>:8500/v1/agent/service/deregister -
Service Definition 샘플
**service** { id = "red0" # 서비스 ID 로 유일해야 하며 보통 노드 hostname 을 사용 name = "redis" # 서비스명 tags = [ # 서비스에서 사용하는 옵셔널 테그 "primary" ] address = "10.3.13.112" # 서비스의 IP Address port = 6000 # 서비스가 사용중인 포트 checks = [ # 서비스 헬스 체크 { args = ["/bin/check_redis", "-p", "6000"] interval = "5s" timeout = "20s" } ] }- name (required)
- Service 이름
- id
- 서비스 ID 를 지정하는 문자열
- default
- 지정하지 않는 경우 name 값이 사용됨
- tag 와 id 로 Service 를 여러 버전으로 구분 가능
- Service 별로 여러 id 사용 가능
- tags
- Tags
- Service 의 레이블로 version 정보 같은 meta 정보를 넣을 때 사용
- address
- 연결할 Service 의 ip 주소
- NIC 카드가 여러개 있을 때 특정 사용할 IP Address 를 지정
- default
- 지정하지 않는 경우 Consul agent 의 default address 가 사용됨
- port
- Service 실행 port
- checks
- Health checks
- 서비스 Health Check
- name (required)
-
- Query Service
-
Consul Client 는 사용자가 등록한 Service 를 Service Catalog 에 저장
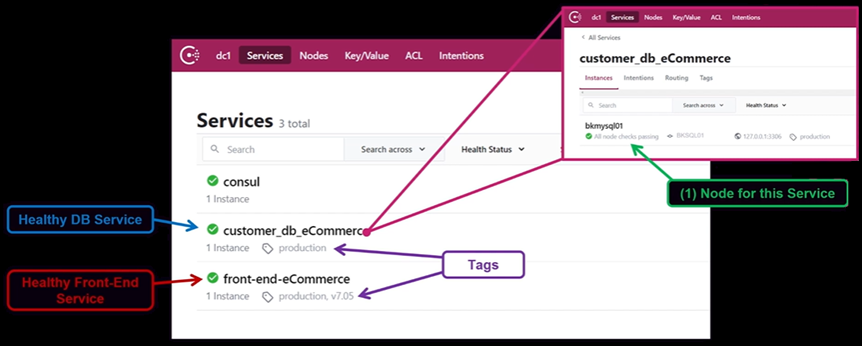
-
Service Catalog 를 통해 DNS Query 가능
# Server Side $ cd /etc/consul.d $ cat <<EOF > web1.json { "service": { "name": "web", "id": "web1", "port": 8080, "tags": ["v1"] } } EOF $ cat <<EOF > web2.json { "service": { "name": "web", "id": "web2", "port": 9080, "tags": ["v2"] } } EOF $ consul reload # 서비스 조회 형식 # Consul 의 DNS 인터페이스는 디폴트로 8600 포트를 사용 # [<tag>.]**<service>.service**[.<datacenter>.dc][.<cluster-peer>.peer][.<sameness-group>.sg].**<domain>** $ dig @localhost -p 8600 web.service.consul SRV ... ;; ANSWER SECTION: web.service.consul. 0 IN SRV 1 1 8080 consul-client-2.node.dc1.consul. web.service.consul. 0 IN SRV 1 1 9080 consul-client-2.node.dc1.consul. .... $ dig @localhost -p 8600 v1.web.service.consul SRV ... ;; ANSWER SECTION: v1.web.service.consul. 0 IN SRV 1 1 8080 consul-client-2.node.dc1.consul. ....- dig 명령어 사용법
- dig -p [port] @[server] [domain] [type] [filter]
- server
- 확인할 때 사용할 네임 서버를 지정한다.
- 지정하지 않으면 /etc/resolv.conf 에 등록된 Nameserver 를 이용하여 Root 서버를 조회한다.
- type
- a/mx/ns/soa/srv/any
- filter
- +short
- 응답 부분만 보기
- +trace
- 추적 과정도 보기
- +short
- server
- dig -p [port] @[server] [domain] [type] [filter]
- dig 명령어 사용법
-
- Monitoring Service
- 문제가 생긴 node 나 service 를 모니터링 하여 문제가 없는 Node 나 Service 만 선별하여 Service 를 찾거나 건강한 Service 에만 트래픽을 보내도록 돕는 기능
-
예시
$ cd /etc/consul.d/ $ sudo vi consul.hcl data_dir = "/etc/consul.d/consul-dir" start_join = ["3.35.43.234"] bind_addr = "0.0.0.0" advertise_addr = "52.79.247.105" node_name = "consul-client-1" $ sudo systemctl restart consul $ sudo vi web.json { "service": { "name": "web", "port": 80, "check": { "args": [ "curl", "127.0.0.1" ], "interval": "10s" } } } $ consul validate /etc/consul.d $ consul reload Configuration reload triggered # Web Service 사용하는 App 설치 $ sudo amazon-linux-extras install -y nginx1 $ nginx -v $ sudo systemctl start nginx # nginx 중지 $ sudo systemctl stop nginx # Consul UI 에서 Service Catalog 확인 혹은 API 를 통해 확인 // GET /health/node/:node $ curl \ -H "X-Consul-Namespace: *" \ http://127.0.0.1:8500/v1/health/node/my-node [ { "ID": "40e4a748-2192-161a-0510-9bf59fe950b5", "Node": "foobar", "CheckID": "serfHealth", "Name": "Serf Health Status", "Status": "passing", "Notes": "", "Output": "", "ServiceID": "", "ServiceName": "", "ServiceTags": [], "Namespace": "default" }, { "ID": "40e4a748-2192-161a-0510-9bf59fe950b5", "Node": "foobar", "CheckID": "service:redis", "Name": "Service 'redis' check", "Status": "passing", "Notes": "", "Output": "", "ServiceID": "redis", "ServiceName": "redis", "ServiceTags": ["primary"], "Namespace": "foo" } ] //GET /health/checks/:service $ curl \ http://127.0.0.1:8500/v1/health/checks/my-service?ns=default [ { "Node": "foobar", "CheckID": "service:redis", "Name": "Service 'redis' check", "Status": "passing", "Notes": "", "Output": "", "ServiceID": "redis", "ServiceName": "redis", "ServiceTags": ["primary"], "Namespace": "default" } ]
- Register Service
Consul 통신 보안
- Gossip Encryption (8301 TPC/UDP)
- Gossip 통신(Consul 서버 사이의 데이터 공유 프로토콜) 시의 암호화
- 대칭키를 통한 암호화
- RPC Encryption
- Server 와 Client 사이의 Encryption
- TLS 통신
- Mesh Encryption
- Consul Connect 에 의해 제공됨
- Service Mesh 구성에서 Proxy 사이에 Encryption, Authenticity
- mutual TLS 통신
Gitlab 에서 Consul 노드 구성
- Gitlab Consul
- GitLab 프리미엄에는 Consul의 번들 버전이 포함되어 있어
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb을 사용하여 관리할 수 있는 서비스 디스커버리가 제공됨
- GitLab 프리미엄에는 Consul의 번들 버전이 포함되어 있어
- 전제 조건
- Consul을 설정하려면 GitLab Self-Managed Premium 또는 Ultimate 버전에서 제공되는 내장 Consul을 사용해야 함
- Consul 서버 노드 수를 결정해야 함
- 필요한 포트가 방화벽에서 열려 있는지 확인
- 8500, 8501
- Consul Node 구성
- Server
- GitLab 설치: GitLab을 설치하되
EXTERNAL_URL값을 입력하지 않음 -
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb 수정
# Consul 역할만 활성화 # 10.0.10.100 10.0.11.100 10.0.12.100 는 Consul Server 의 IP roles ['consul_role'] consul['enable'] = true consul['monitoring_service_discovery'] = true consul['configuration'] = { server: true, retry_join: %w(10.0.10.100 10.0.11.100 10.0.12.100), ui: true, datacenter: 'gitlab_consul', client_addr: '0.0.0.0', } ... -
GitLab 재구성
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure -
Consul 상태 확인
sudo /opt/gitlab/embedded/bin/consul members -
정상적인 출력 예시
Node Address Status Type Build Protocol DC CONSUL_NODE_ONE XXX.XXX.XXX.YYY:8301 alive server 0.9.2 2 gitlab_consul CONSUL_NODE_TWO XXX.XXX.XXX.YYY:8301 alive server 0.9.2 2 gitlab_consul CONSUL_NODE_THREE XXX.XXX.XXX.YYY:8301 alive server 0.9.2 2 gitlab_consul
- GitLab 설치: GitLab을 설치하되
-
Client
consul['enable'] = true consul['monitoring_service_discovery'] = true consul['configuration'] = { retry_join: %w(10.0.10.100 10.0.11.100 10.0.12.100), }
- Server
- Consul 노드 TLS 설정
-
기본적으로 TLS는 활성화되지 않으며, 기본 구성은 다음과 같음
... consul['use_tls'] = false consul['tls_ca_file'] = nil consul['tls_certificate_file'] = nil consul['tls_key_file'] = nil consul['tls_verify_client'] = nil - TLS를 활성화하려면
consul['use_tls'] = true로 설정하고, 추가 구성도 필요- 서버 노드에서 TLS 설정
- 서버 노드는 최소한
tls_ca_file,tls_certificate_file,tls_key_file을 설정해야 함
- 서버 노드는 최소한
- 클라이언트 노드에서 TLS 설정
- 클라이언트 노드는 기본적으로 서버에서 TLS 인증을 요구하지 않음
- 서버에서 클라이언트 인증을 비활성화하려면
consul['tls_verify_client'] = false로 설정할 수 있음
- 서버 노드에서 TLS 설정
- TLS 설정 예시
- 최소 TLS 지원
- 서버는 TLS로 수신 요청을 처리하되, 클라이언트 인증은 요구하지 않는 경우
-
서버 노드 구성 (/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb)
... consul['use_tls'] = true consul['tls_ca_file'] = '/path/to/ca.crt.pem' consul['tls_certificate_file'] = '/path/to/server.crt.pem' consul['tls_key_file'] = '/path/to/server.key.pem' consul['tls_verify_client'] = false consul['https_port'] = 8501 -
클라이언트 노드 구성
... consul['enable'] = true consul['use_tls'] = true consul['tls_ca_file'] = '/path/to/ca.crt.pem' consul['https_port'] = 8501 # patroni 인스턴스 설정시 patroni['consul']['url'] = 'https://localhost:8501' -
GitLab 재구성
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
-
- 서버는 TLS로 수신 요청을 처리하되, 클라이언트 인증은 요구하지 않는 경우
- 기본 TLS 지원
- 서버에서 상호 TLS 인증을 사용하는 경우
-
서버 노드 구성 (/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb)
... consul['use_tls'] = true consul['tls_ca_file'] = '/path/to/ca.crt.pem' consul['tls_certificate_file'] = '/path/to/server.crt.pem' consul['tls_key_file'] = '/path/to/server.key.pem' consul['https_port'] = 8501 -
클라이언트 노드 구성
. consul['use_tls'] = true consul['tls_ca_file'] = '/path/to/ca.crt.pem' consul['tls_certificate_file'] = '/path/to/client.crt.pem' consul['tls_key_file'] = '/path/to/client.key.pem' consul['https_port'] = 8501 # patroni 인스턴스 설정시 patroni['consul']['url'] = 'https://localhost:8501' -
GitLab 재구성
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
-
- 서버에서 상호 TLS 인증을 사용하는 경우
- 전체 TLS 지원 (서버 및 클라이언트 상호 TLS 인증)
- 서버, 클라이언트 및 Patroni 클라이언트 인증서를 동일한 CA로 발급해야 상호 TLS 인증이 가능
-
서버 구성 (/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb)
... consul['use_tls'] = true consul['tls_ca_file'] = '/path/to/ca.crt.pem' consul['tls_certificate_file'] = '/path/to/server.crt.pem' consul['tls_key_file'] = '/path/to/server.key.pem' consul['https_port'] = 8501 -
클라이언트 구성
... consul['use_tls'] = true consul['tls_verify_client'] = true consul['tls_ca_file'] = '/path/to/ca.crt.pem' consul['tls_certificate_file'] = '/path/to/client.crt.pem' consul['tls_key_file'] = '/path/to/client.key.pem' consul['https_port'] = 8501 patroni['consul']['url'] = 'https://localhost:8501' patroni['consul']['cacert'] = '/path/to/ca.crt.pem' patroni['consul']['cert'] = '/opt/tls/patroni.crt.pem' patroni['consul']['key'] = '/opt/tls/patroni.key.pem' patroni['consul']['verify'] = true -
GitLab 재구성
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
-
- 서버, 클라이언트 및 Patroni 클라이언트 인증서를 동일한 CA로 발급해야 상호 TLS 인증이 가능
- 최소 TLS 지원
-
- Consul 노드 Gossip Encryption 설정
- Consul 에이전트 간의 통신을 보호하기 위해 암호화키 사용 설정 가능
- 설정 방법
-
gitlab 설치 후 encryption key 생성
$ gitlab-ctl consul keygen -
gitlab.rb 파일 수정
consul['encryption_key'] = <base-64-key> consul['encryption_verify_incoming'] = true consul['encryption_verify_outgoing'] = true -
reconfigure
$ sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
-
-
Consul Service 명 설정
praefect['consul_service_name'] = 'praefect' gitaly['consul_service_name'] = 'gitaly' gitlab_exporter['consul_service_name'] = 'gitlab-exporter' postgres_exporter['consul_service_name'] = 'postgres-exporter' redis_exporter['consul_service_name'] = 'redis-exporter' postgres_exporter['consul_service_name'] = 'postgres-exporter' prometheus['consul_service_name'] = 'prometheus' nginx['consul_service_name'] = 'nginx' sidekiq['consul_service_name'] = 'sidekiq' puma['consul_service_name'] = 'rails' gitlab_workhorse['consul_service_name'] = 'workhorse' -
Gitlab Service DNS 조회
dig A praefect.service.consul @127.0.0.1